Fucoidan, also known as fucoidan or fucoidan, is a type of sulfated polysaccharide extracted from the cell walls of brown algae. It is widely found in brown algae such as kelp, wakame, and bubblylea, as well as echinoderms like sea cucumbers. As a marine biological resource with a unique structure and diverse biological activities, fucoidan shows broad application prospects in food, medicine, and cosmetics.
Structurally, fucoidan is mainly composed of α-L-fucose residues linked by glycosidic bonds. Its sugar chains also contain sulfate groups, the position and content of which play a crucial role in its biological activity. Fucoidan from different sources exhibits differences in sugar chain length, branching degree, sulfation degree, and sulfate group substitution positions. It is precisely this structural diversity that endows fucoidan with a wide range of biological activities, making it a focus of research in the life sciences.
Applications in the Pharmaceutical Field
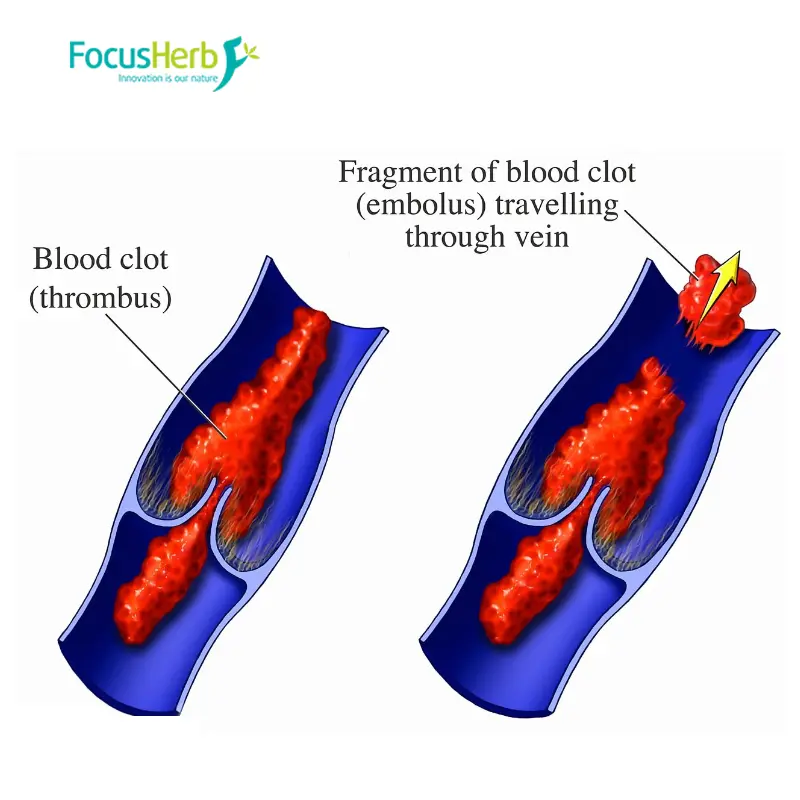
(I) Anticoagulation and Antithrombosis
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, seriously threatening human health. Anticoagulants are among the most important drugs for the prevention and treatment of thrombotic diseases in clinical practice. The National Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Natural Products, Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with the National Key Laboratory of Natural and Bionic Drugs, Peking University, constructed a compound library containing 58 structurally defined sulfated fucoidans. Their anticoagulant activity, structure-activity relationship, and mechanism were studied, leading to the discovery of novel anticoagulant molecules with anticoagulant activity comparable to heparin but with different anticoagulant mechanisms.
Natural fucoidan is a class of sulfated polysaccharides extracted from brown algae, attracting significant attention due to its anticoagulant activity. Studies have found that molecular size and the degree of sulfation are key factors affecting the anticoagulant activity of fucoidan. Some compounds with specific structures exhibit strong anticoagulant activity, significantly prolonging the partially activated thromboplastin time in human plasma without affecting prothrombin time or thrombin time. Mechanistic studies showed that these compounds did not significantly inhibit the activity of coagulation factors FXa and FIIa, but selectively inhibited the intrinsic factor FXase, unlike the anticoagulation mechanism of clinical heparin drugs. This novel type of fucoidan selectively inhibits the intrinsic coagulation pathway associated with pathological thrombosis without affecting extrinsic and common coagulation pathways, potentially reducing bleeding risk and becoming a safer candidate molecule for anticoagulation therapy.
Researchers at Guangdong Ocean University discovered through experiments that Sargassum fucoidan can inhibit thrombus formation in mice and has a preventive effect. The purified fucoidan component showed a more significant inhibitory effect on mouse thrombosis and prolonged clotting time. These studies indicate that fucoidan has potential application value in the fields of anticoagulation and antithrombosis, and is expected to be developed into novel anticoagulant drugs or functional foods for the prevention and treatment of thrombosis-related diseases.
(II) Immune Regulation
Fucoidan plays an important role in immune regulation, activating immune cells, regulating immune responses, and enhancing the body’s immunity. Studies have shown that fucoidan can promote the proliferation and differentiation of immune cells such as T cells and macrophages. T cells act as “commanders” in the immune system, responsible for recognizing and clearing foreign pathogens; macrophages act as “scavengers,” engulfing and digesting pathogens and harmful substances. Fucoidan significantly enhances the overall defense capabilities of the immune system by increasing the number and activity of these key immune cells.
Furthermore, fucoidan can activate immune response mechanisms, inducing immune cells to produce cytokines and antibodies through multiple pathways, enhancing the ability of immune cells to recognize and attack pathogens, improving the speed of the immune system’s response and the efficiency of pathogen clearance, and helping to prevent and treat various infectious diseases. Simultaneously, the balance of the immune system is crucial for maintaining human health. Fucoidan has the ability to regulate immune balance; it can inhibit overactive immune responses, preventing the occurrence of autoimmune diseases; and enhance the regulation of weak immune responses, improving the immune system’s resistance to pathogens. Based on its excellent immunomodulatory effects, fucoidan shows great potential in the development of immunomodulatory drugs, and is expected to become an effective ingredient for enhancing the body’s immunity and preventing and treating immune-related diseases, bringing new therapeutic ideas and methods to the field of immunomodulation.
(III) Anti-tumor adjuvant therapy
In anti-tumor research, fucoidan has shown many positive effects. Numerous research results have shown that fucoidan can inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells, induce tumor cell apoptosis, and inhibit tumor angiogenesis, thereby hindering tumor growth and metastasis. Japanese research suggests that the special mechanism by which fucoidan helps fight cancer includes stimulating abnormal cell proliferation (apoptosis), preventing new blood vessel formation, and strengthening the immune system. Research published by Case Western Reserve University in the United States shows that the novel natural functional ingredient fucoidan has a good assisted effect in inhibiting the development of melanoma. Combining lapatinib with fucoidan can achieve an 85% inhibition rate of melanoma proliferation and can also eliminate the side effects of long-term lapatinib use. Related experiments have found that fucoidan can kill tumors by regulating Th1 cells and natural killer cells; it can significantly enhance the cytotoxic activity of peritoneal macrophages in mice, thereby destroying and eliminating tumor cells; it can also significantly improve the proliferation capacity of T and B lymphocytes, the phagocytic function of macrophages, and the serum hemolysin content in irradiated rats, enhance delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions in rats, and inhibit apoptosis of splenic lymphocytes after irradiation. These mechanisms of action indicate that fucoidan can fight tumors by activating the body’s own immune system.
In addition, fucoidan can be used in combination with chemotherapy drugs to improve the efficacy of chemotherapy and reduce the side effects of chemotherapy drugs. For example, combining fucoidan with chemotherapy drugs to form nanoparticles can not only stabilize the nanocarrier but also increase the anticancer activity of chemotherapy drugs, achieving systemic treatment of tumors. Therefore, fucoidan, as a potential antitumor adjuvant, has broad application prospects and provides new strategies and methods for tumor treatment.
(IV) Other Medical Efficacy
In addition to the above important pharmaceutical applications, fucoidan has also shown unique efficacy and research progress in other medical fields. In terms of liver protection, studies have found that fucoidan can alleviate liver damage, protect hepatocytes, and promote liver repair and regeneration, exhibiting certain protective effects against alcoholic and drug-induced liver injury. Its mechanism of action may be related to the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of fucoidan.
In the field of neuroprotection, research from Shandong University has for the first time confirmed that fucoidan can promote the proliferation of neural stem/prototype cells (NSPCs) and has a synergistic effect with fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), without inducing apoptosis. Preliminary findings indicate that the proliferative and aggregation-promoting effects of fucoidan on NSPCs are related to the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. This provides new hope for nerve injury repair and the treatment of nervous system diseases.
Regarding gastric ulcers, a joint study conducted by Capital Normal University and other institutions showed that fucoidan has a certain protective effect against acute alcoholic gastric mucosal injury in rats. Its mechanism may be related to enhancing gastric mucosal protective factors, improving antioxidant capacity, and reducing lipid peroxidation capacity, providing a new natural drug option for the treatment of gastric ulcers. In addition, studies have reported that fucoidan has potential applications in the treatment of diseases such as tuberculosis. Although related research is still in the exploratory stage, it has shown promising prospects. With further research, fucoidan is expected to play an important role in the treatment of more diseases.
Applications in the Food Industry
(I) Functional Food Additives
Fucoidan, as a component with unique bioactivity, is gradually emerging in the field of functional food additives. It can significantly enhance the health value of products and meet consumers’ pursuit of healthy eating. Adding fucoidan to yogurt not only adds a unique taste but also plays a role in regulating intestinal flora, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, inhibiting the reproduction of harmful bacteria, and maintaining the balance of intestinal microecology, thereby improving intestinal health. Adding fucoidan to beverages can not only enhance the antioxidant capacity of beverages, helping the body to eliminate free radicals and reduce oxidative damage, but also, due to its blood sugar and blood lipid lowering functions, provide healthier beverage options for people concerned about blood sugar and blood lipid health, which is of great significance for the prevention and control of chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
(II) Antioxidants and Preservatives
Oxidation is one of the main factors leading to the decline in food quality during food processing and storage. Fucoidan is rich in polyphenolic compounds, which are powerful free radical scavengers that can effectively remove free radicals in the body and reduce oxidative damage. Fucoidan can be used as a natural antioxidant to extend the shelf life of food and maintain its freshness and nutritional value.
When applied to oil-rich foods, fucoidan exerts its antioxidant effects through multiple pathways. Certain functional groups in the fucoidan molecule, such as hydroxyl and sulfate groups, can donate hydrogen atoms or electrons to combine with free radicals generated during oil oxidation, transforming them into stable molecules. This interrupts the chain reaction of free radicals and prevents further oxidative rancidity of the oils. Fucoidan can also bind to metal ions in food, reducing their ability to catalyze oxidation reactions, further improving the antioxidant stability of the food and better preserving its flavor and quality.
 Applications in the Cosmetic Industry
Applications in the Cosmetic Industry
Fucogran has demonstrated unique efficacy in the cosmetic field, becoming a key ingredient in many high-end cosmetics. Researchers at the School of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Jiangnan University, discovered through hygroscopic and moisturizing tests that, under different humidity conditions, fucogran exhibits superior hygroscopic and moisturizing properties compared to commonly used raw materials such as glycerin, butylene glycol, and sodium alginate, making it an excellent natural moisturizer for use in skincare products.
As a novel moisturizer, fucogran possesses strong hydration capabilities, absorbing water even in low-humidity environments. It exhibits excellent moisturizing and wetting properties, forming a breathable protective film on the skin surface, reducing transepidermal water loss, enhancing stratum corneum hydration, improving dry skin problems, and providing continuous hydration. Simultaneously, it also possesses certain anti-wrinkle effects, promoting collagen synthesis, enhancing skin elasticity, reducing wrinkles, and delaying skin aging. Fucoogran also demonstrates outstanding skin repair capabilities. It can stimulate fibroblast proliferation, accelerate epidermal renewal and dermal collagen synthesis, and has a significant repairing effect on damaged skin, helping it return to a healthy state. In terms of soothing the skin, fucoidan can act as an antibody against various viruses, possessing anti-inflammatory properties that effectively reduce skin inflammation, alleviate discomfort, and enhance the skin’s resistance. Furthermore, fucoidan provides a soft, silky, and pleasant skin feel. When used in hair creams, it imparts shine and moisture to hair. Therefore, it is widely used in various cosmetics such as moisturizers, body lotions, eye gels, makeup removers, toners, sunscreens, and shampoos, offering consumers a superior skincare experience.
Applications in Agriculture and Feed
(I) Aquaculture Feed Additives
In aquaculture, fucoidan has demonstrated significant advantages as a feed additive. Researchers conducted experiments by adding fucoidan to shrimp feed, with surprising results. In a study of Penaeus monodon, adding fucoidan from the polycystic cysts of the brown seaweed Sargassum significantly improved the survival rate of shrimp infected with White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV). This discovery provides new ideas and methods for shrimp farming, and is expected to effectively reduce disease losses during the farming process and improve farming efficiency.
From the perspective of mechanism of action, fucoidan can activate the non-specific defense system of farmed animals and enhance immune activity. Key immune indicators such as total blood cell count and phenol oxidase activity are significantly improved under the action of fucoidan, thereby enhancing the immunity of farmed animals and better resisting the invasion of pathogens. Fucoidan can also promote the growth of farmed animals, improve their digestive capacity, increase feed utilization, and provide comprehensive support for the healthy growth of farmed animals.
(II) Other Potential Agricultural Uses
Besides its application in aquaculture feed, fucoidan has other potential uses in agriculture. Fucoidan plays a unique role in improving soil structure. It increases soil cohesion, enhances water and fertilizer retention capacity, improves soil aeration, and creates a favorable environment for plant root growth. This not only helps improve soil fertility but also reduces soil erosion, promoting sustainable agricultural development.
Fucoidan may also have a positive impact on plant growth. Studies have shown that fucoidan can promote seed germination, increase germination rate and vigor, and make seedlings stronger. During plant growth, fucoidan can regulate plant growth hormone levels, promote root growth and above-ground development, improve plant stress resistance, and enhance resistance to adverse conditions such as drought, salinity, and pests. Although current research is still in the exploratory stage, the potential of fucoidan in agriculture undoubtedly provides a new direction for innovative development in agricultural production.
Industrial Applications
(I) Chemical Raw Materials
In the chemical industry, fucoidan has unique application value, especially in the synthesis of polymer materials. The sulfate groups in the fucoidan molecule are key to its special role. These sulfate groups have high reactivity and can undergo cross-linking reactions with other compounds. In the synthesis of certain polymer materials, fucoidan can participate in the reaction as a cross-linking agent, forming a three-dimensional network structure by binding with the active sites on the polymer molecular chains. This cross-linking structure can significantly improve the performance of polymer materials, giving them better stability, mechanical strength, and chemical corrosion resistance.
Taking the synthesis of bioplastics as an example, adding an appropriate amount of fucoidan during the preparation process allows the sulfate groups of fucoidan to undergo cross-linking reactions with the active groups in the plastic raw materials, resulting in tighter connections between the plastic molecular chains. This improves the strength and flexibility of bioplastics, making them more durable in practical applications, expanding the application range of bioplastics, and meeting the material performance requirements of more fields.
(II) Other Industrial Application Possibilities
In the metal processing industry, fucoidan has shown unique advantages as an additive. Adding fucoidan to metalworking fluids allows it to form a uniform and dense protective film on the metal surface. This film acts like a “protective suit” for the metal, effectively isolating it from the external environment, thus significantly slowing down the oxidation rate during processing, reducing the risk of corrosion, and improving the quality and lifespan of metal products.
Adding fucoidan to lubricants also greatly enhances their performance. The molecular structure of fucoidan gives it excellent lubricity, effectively reducing the coefficient of friction. When applied to the lubrication of machinery, it reduces friction and wear between parts, acting like a smooth “pad” between components, making the machinery run more smoothly, reducing energy consumption, extending equipment maintenance cycles and lifespan, and improving production efficiency.
In the textile industry, fucoidan also has potential applications. It can be used as a raw material or additive for textile auxiliaries. Adding fucoidan during fiber processing enhances the bonding force between fibers and auxiliaries, allowing the auxiliaries to better adhere to the fiber surface, improving processing efficiency and product quality. During the fabric finishing stage, fucoidan can give fabrics a soft and smooth feel, improve the comfort of wearing them, and may also enhance the antistatic properties of the fabric, reducing the impact of static electricity on the use of the fabric and bringing consumers a better wearing experience.

With continuous research and technological advancements, the application prospects of fucoidan will become even broader. In the future, we can expect to see fucoidan used in more fields, bringing greater benefits to human health and life. However, the research and application of fucoidan still face some challenges, such as optimizing extraction techniques, reducing costs, and conducting in-depth research on its mechanism of action. It is believed that with the joint efforts of researchers and enterprises, these problems will be gradually solved, the application potential of fucoidan will be further explored, and it will make a greater contribution to promoting the development of various industries.
Previous: Apigenin:Small matter, big energy






















 Applications in the Cosmetic Industry
Applications in the Cosmetic Industry